Vehicle lug nuts are an intricate part of your wheel system. Lug nuts are often overlooked and not taken into consideration. Ironically, it is an essential feature that holds a wheel to your car. Lug nuts center each wheel onto the vehicle and provide an even contact surface all around. In this article, we will discuss the technical specifications of lugs nuts, along with our recommendations and installation practices.
Technical Specifications
Lug nuts are categorized into three significant specifications: seat type, thread size, and thread pitch.
Seat Type
There are five most common seat types used for lug nuts on the market today:
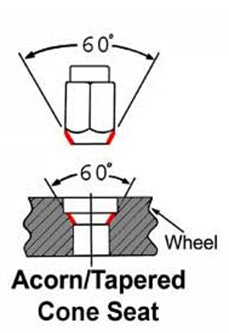
- Conical: Regarded as one of the most common types of lug nuts. A conical seat is often referred to as "tapered" or "acorn" style lug nut and come standard in a 60° or 45° taper. The 60° taper is on most aftermarket wheels and is relatively widespread. In comparison, the 45° taper has a wider surface area contact, which engages with the wheel more securely.
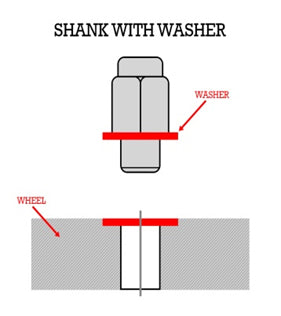
- Shank Style: Often called the "Mag Type" seat, this lug nut features a washer for a tight and direct fit. Apart from the washer, the 'shank,' which is essentially an extended thread, is inserted into the hole. Unlike with the conical seat types, the shank style lug nut is designed to be flush against the wheel.
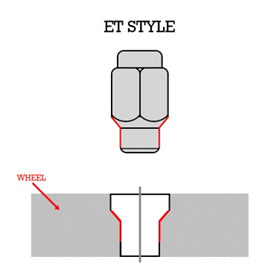
- ET Style: ‘Extra Threads’ style of lug nuts is mostly found on older vehicles onto which new aluminum wheels present. Because older vehicles used thinner steel wheels, the ET style lug nuts make up for the vehicles with short studs. ET Style lug nuts use a 60° conical seat with an extended shank for additional threading.
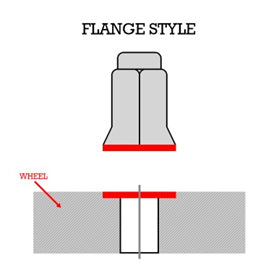
- Flange Style: A Flange Style lug nut is a seat type that acquires a flange that contacts a recess on the wheel around the stud. This type of lug nut resides on ATV's and Go-karts. Most vehicles do not have a recess on the wheel for this type of lug nut to make a secure fit, so avoid use if incompatible.
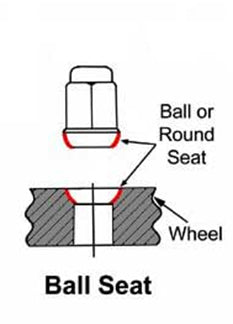
- Ball Seat: Also known as the 'spherical' seat type, this lug nut features a hex head with a rounded or dome-like construction to make contact with the wheel's surface. The ball seat type lug nuts are standard on European vehicles that do not use a lug bolt set up.
Thread Sizes
Lug nuts come in various sizes, depending on which vehicle you have and the studs that are present on that vehicle. You must get the correct size for your vehicle to avoid any safety or incompatibility issues.
In the following list, the first number depicts the diameter of the stud, while the second number corresponds to the thread pitch.
ISO Standard Lug Sizes:
- M12 x 1.25
- M12 x 1.5
- M12 x 1.75
- M14 x 1.25
- M14 x 1.5
- M14 x 2.0
- M16 x 1.5
- M16 x 2.0
UN-series Lug Sizes
- 3/8" - 24 UNF
- 7/16" - 20 UNF
- 1/2" - 20 UNF
- 9/16" - 18 UNF
Thread Pitch and Engagement
Thread pitch is essentially the distance in millimeters between each thread. It is important to note because it corresponds to the sizes that lug nuts come in (the second number we’ve talked about). As per proper engagement, it is paramount that you have a minimum thread engagement as per the vehicle stud's diameter. For example, if your vehicle's stud size is ½" then you will need a minimum of ½" of threads into the lug nut.
Why Are Some Lug Nuts More Expensive?
There have been questions surrounding why some are more expensive than others. In addition to the different seat type lug nuts explained previously, there are more costly options, which are reserved more for speed purposes and car enthusiasts.
Examples of such type lug nuts include: closed-end, open-ended, locking style, and two-piece lug nuts.
Closed-end lug nuts feature wheel stud not exposed ends and are the most common type. The closed-end construction gives off a clean appearance and provides pleasing aesthetics. An example of this type is our Muteki Closed End Lug Nuts.
Open-ended lug nuts are also very common. Open-ended refers to having an opening at the lug nut's head for the stud to protrude or be visible through. This setup is typical for vehicles with extended wheels studs that bottom out the threading on the lug nut. A great line of products to consider for open-ended lug nuts are the Muteki Short Open-End Lug Nuts and Blox Lug Nuts.
Locking style lug nuts require a special key to prevent wheel theft. This construction raises the unit's price tremendously because it acquires a built-in safety feature that prevents your wheels from being tampered with or stolen. Check out our Project Kics R40 and Project Kics R26 to see these types of lug nuts.
Project Kics R40 Lug Nuts

Project Kics R26 Lug Nuts
Two-piece lug nuts come either with a rotating base or a shell type. A rotating base two-piece lug nut is a spherical seat that rotates upon installation. This type prevents you from scratching your wheels and keeping your lug nuts looking clean and new at all times. The shell type two-piece lug nut gives the outer shell the ability to come off, which also serves the same purpose of keeping your lug nuts scratch-free. Check out our Project Kics R40 and Project Kics R26 to see these types of lug nuts.
Expensive lug nuts are also lightweight and typically made from high-quality materials, a good example of expensive lug nuts is the ones made from titanium or composite. Titanium or composite lug nuts are generally the most costly. They possess considerably high yield strength compared to other lug nuts like those made from aluminum and steel.
Another reason is its resistance in thread separation that involves tightening and losing. Expensive lug nuts are known for their durability in intact threading that won't strip easily. This construction also gives the threading a high wear resistance that the lug nut continually undergoes. These two factors of high yield strength and hardness ratings are critical and even used in aircraft structure.
Moreover, while other lug nuts may rust with time, which affects their appearance, expensive lug nuts are known to be rustproof. Hence, they last longer without being subjected to scratches or discoloration.
Installation and Recommendations
Last but not least, proper installation is significant in having lug nuts that function correctly as intended. Most lug nuts require you to refer to your vehicle's manual to ensure you have the proper torque specifications embedded onto each lug nut.
It is crucial to always use a torque wrench when installing any type of lug nut. Making sure you have proper torque on the lug nuts allows for even pressure on all four sides of the vehicle. Proper torque also ensures that the lug nuts are not over torqued or under torqued, causing compromise in their structural integrity.
In addition, during installation, we recommend being overly keen on utilizing the star pattern method. This method includes tightening each lug nut in a star-shaped order to prevent over-torqueing or a torque imbalance on the wheel.


